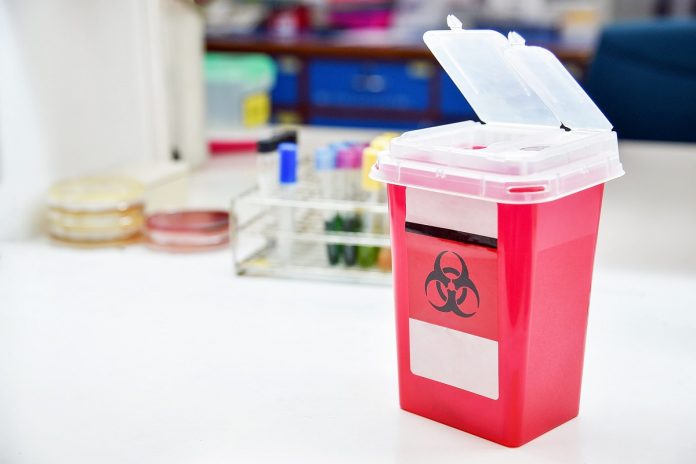
Riverside County Medical Waste Disposal – Medical waste is a subset of waste produced in healthcare facilities. It includes hospitals, doctor dentists’ office’s blood banks, clinics for veterinary medicine, and medical research laboratories and facilities. Medical waste generally refers to medical waste that could be affected by body fluids, blood, or other materials. It could be infectious and is commonly called regulated medical waste. Waste contaminated with biological agents and any sharps that are uncontaminated or not.
Table of Contents
Examples:
- Microbiological culture.
- Human cell culture.
- Human blood, blood products, as well as blood components.
- All disposable lab ware that has been contaminated (culture dishes, Pipet tips, tubes, dishes).
- Medical specimens (human blood and other potentially infectious substances).
- All needles and Syringes.
Biohazardous garbage (except “sharps”) that has been autoclaved can be recycled as General Waste by Riverside County Medical Waste Disposal. However, autoclaved junk in bags with biohazardous markings or labels placed in the buildings’ dumpsters for disposal can create problems with removal.
When disposing of autoclaved wastes in the dumpster of the building, make sure there are no biohazardous marks or labels evident. The autoclave material must be placed in an opaque plastic bag to be disposed of as General Waste.
Guideline by Riverside County Medical Waste Disposal
Don’t autoclave chemical or radioactive wastes. Do not put radioactive or chemical wastes in hazardous biohazardous “burn boxes.” Non-radioactive, decontaminated liquids must be flushed down the drain using plenty of water. Do not let the outside part of “the “burn box” protect the personnel who handle boxes from exposure to harmful agents.
Packaging Guidelines:
When disposing of “Sharps” (needles, syringes, scalpel blades, etc.)
Place all intact “sharps,” whether contaminated or not, in a puncture-resistant “sharps” container. The containers can bring at Chemistry Stores or laboratory safety equipment suppliers.
Don’t bend, recapture or remove needles. Place all intact “sharps,” whether contaminated or not, in a puncture-resistant “sharps” container. The containers can bring at Chemistry Stores or laboratory safety equipment suppliers like Riverside County Medical Waste Disposal.
Don’t Bend, Recapture or Remove Needles.
Fill to 3/4 and then close the lid and secure it with tape. Filling too much or forcing it to be filled could cause wounds to be punctured. Don’t overfill.
Non-Sharp Solid Waste For Autoclave:
Recycle non-sharp biological waste within autoclavable plastic bags. Autoclave bags are preferred to be transparent or white (not orange or red). They do not contain the term “biohazardous” or the universal symbol for biohazardous materials.
Place the bags filled with bags in the autoclave pan to transport them from the lab to the autoclave. Add 250mL of water into the bag, then seal it loosely, allowing the steam to escape while allowing air to be able to. The pan and load should be autoclaved at 121°C for 1 hour. Let the pan and autoclaved product be fantastic. Place autoclaved bags in garbage cans lined with opaque, heavyweight plastic bags. After that, transfer them to the building dumpster.
Non-Sharp Solid Waste For Incineration:
Place the waste inside a plastic liner in an environmentally hazardous trash box (“burn box”) provided by Riverside County Medical Waste Disposal. Double bag the wet material and place an absorbent material inside the bag.
The plastic bag is twisted. Twist it around the bag(s) on top. Bend the twist to create an elongated loop. Seal using tape. Seal the bags separately in double bagging—the box to the box using video. Indicate the unique tracking number, given through the Riverside County Medical Waste Disposal System, on the container to be taken away and disposed of.
Contained Glass, As Well As Pasteur Pipets:
The Glass That Has Been Contaminated Can Be Treated With Any of The Two Techniques:
Clean the Glass by autoclaving or taking it to the bleach bath for 30 minutes. After which, put it in a solid cardboard box, seal it with tape, and place the tube into the construction dumpster. Glass that has been contaminated can be thrown away into a sharps container and treated according to the guidelines in “Sharps.”
Liquid Wastes:
In general, apply household bleach to an ultimate level of 10 percent, then wait 30 minutes before washing in the sink with large quantities of water. Another option is a disinfectant that has been proven effective against bacteria and can be added to a proper concentration. Wait for 30 minutes before washing the sink using copious amounts of water.
Animal Carcasses:
Place the animal’s carcasses or tissues in bags made of plastic. Double bag any carcasses that are found when there are zoonotic agents present. Place the bag in the freezer until it is removed.