Learn about the causes, symptoms, and impact of fearful-avoidant attachment and discover effective treatment options in this comprehensive guide. Read on to understand the importance of addressing this attachment style and find resources for support.
Anxious or fearful avoidant attachment is a relatively common form of insecure attachment in which those who exhibit it often feel very uncomfortable being close to others. Individuals who got fearful avoidant attachment are quite simply terrified of being abandoned. Just the thought of being alone is enough to make them act more than a little childishly. In this blog post, we will look at what Fearful avoidant attachment is, what its causes are, and possible treatment for it!
Table of Contents
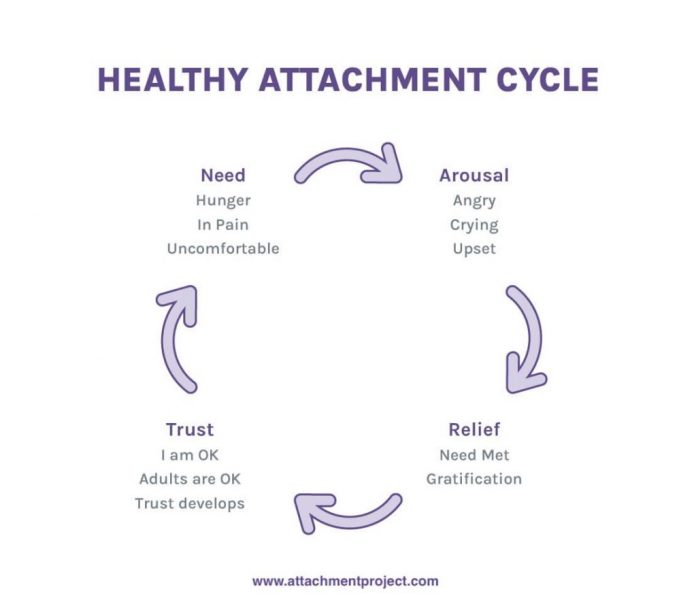
What is a fearful avoidant attachment style?
Fearful avoidant attachment style is a pattern of relating in close relationships that occurs when a person is too anxious or fearful to get close to others. People with this style often have difficulty trusting and depending on other people and may even feel anxious about forming attachments. This can cause them to avoid intimacy in their romantic relationships and also limit their ability to form close friendships.

Individuals who got this attachment may fear rejection, abandonment, or being alone. This fear can lead them to act in ways that push others away or make them appear aloof and distant. They may also worry that others will abandon them if they become too close or dependent on them, and this can cause them to constantly monitor their partners’ actions for any signs of impending rejection or abandonment.
Different types of attachment styles
There are different types of attachments styles, such as:

Anxious attachment
Anxious attachment is characterized by a preoccupation with the availability and responsiveness of the attachment figure. These children are clingy and constantly seek reassurance from their caregivers. Individuals with this attachment are more emotional and can’t calm themselves down when they are upset. They may be averse to being separated from their caregivers and may worry about abandonment.
Avoidant attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by avoidance of closeness to others and rejection of intimacy in relationships. These children tend to have few friends (if any) and have difficulty forming close relationships with peers or romantic partners later in life. They may appear aloof or indifferent to other people’s feelings, but this is because they are uncomfortable with displays of affection or emotions that are not self-generated (such as being comforted).
Secure attachment
People with a secure attachment style can be described as friendly, open, and confident in relationships with others. They have positive self-esteem and aren’t afraid of intimacy with others. They are comfortable getting close to someone else because they know they’ll be okay if that person leaves or becomes unavailable for some reason.
Disorganized attachment
Disorganized attachment is based on a child’s inability to create a coherent sense of self and others. The child does not have any sense of safety and security, which leads to a disorganized attachment style. The child cannot understand that their caregiver is not dangerous but still feels scared when they are around.
This attachment style can cause problems later in life, as adults who have this attachment style are more likely to suffer from PTSD (Post Traumatic Stress Disorder).
Causes of Fearful-Avoidant Attachment
There are many different causes of fearful-avoidant attachment.
- The first that we will discuss is the relationship with the primary caregiver. If the primary caregiver is unavailable or inaccessible, it can lead to fear and avoidance. This can happen when there is abuse or neglect in the home.
- Another cause of fearful-avoidant attachment is poor parenting skills. You should teach your son or daughter how they can interact with others and share their emotions with their friends and family.
- Fearful-avoidant attachment can also be caused by emotional trauma or abuse during childhood. Children who are abused often have trouble forming attachments as adults because they have trust issues from their past experiences with people who should have been trustworthy but weren’t (their parents).
- Finally, fearful-avoidant attachment can also be caused by an individual’s genetic predisposition toward this type of attachment style.
Treatment of fearful avoidant attachment
The key to treating this type of attachment is to build trust and to encourage the person to feel safe enough to express their emotions – both positive and negative.
This means that it’s important not to push them into relationships or situations where they will feel uncomfortable or anxious.
Instead, start with small steps that make them feel safe: asking them what they want in a relationship or what they would like from you as a friend. Ask them how they would like you to respond when they’re upset or sad, and then do it!
If they’re crying, hold them and let them cry until they’ve calmed down. If they’re angry at someone else, let them rant about it for as long as they desire.
Therapy for fearful avoidant attachment
You can also use therapy to treat this attachment style, such as:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – Cognitive Behavioral Therapy teaches people how to change their thinking patterns and behaviors, which ultimately leads to a positive change in their lives. This therapy helps people overcome their fears, anxieties, and phobias by changing how they think about themselves and others around them.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) – EMDR uses eye movements or other forms of stimulation while recalling disturbing memories so that it can process those memories effectively and help you move on from them. This can be very helpful for people who are struggling with fear-avoidant attachment since it helps them process the traumatic experiences from their pasts.
Also Read: iPhone Share Focus Status
Final Words
Lastly, I have to say that, Recognizing attachment styles and learning to manage them can help us all become closer to those we love and heal some of the emotional pain that arises from an unhealthy relationship. The good news is that relationships can be mended, even with bad behaviors, but there needs to be a commitment to change on the part of both parties.